The problem
Frontline Community health workers (CHWs) are essential to achieving health equity for all but are often chronically underinvested in. While a modest amount of training for CHWs is provided through the health system, research conducted by reach52 indicated that additional training and support was identified as a top priority by CHWs. This finding is consistent with external research, which consistently identifies both a need and a desire among CHWs for training and skills development.
Findings suggest that this lack of support for CHWs contributes to high rates of turnover, affecting service provision. A recent study in Philippines examining the role of CHWs in providing connections to primary care concluded that with adequate support and resources to execute their duties, CHWs could increase both community participation and increase their impact in delivering community health services.
Campaign objectives
- To build the “next generation frontline health workers” – community health workers or Agents equipped with the technology, tools and skills to transform the quality of care for their communities.
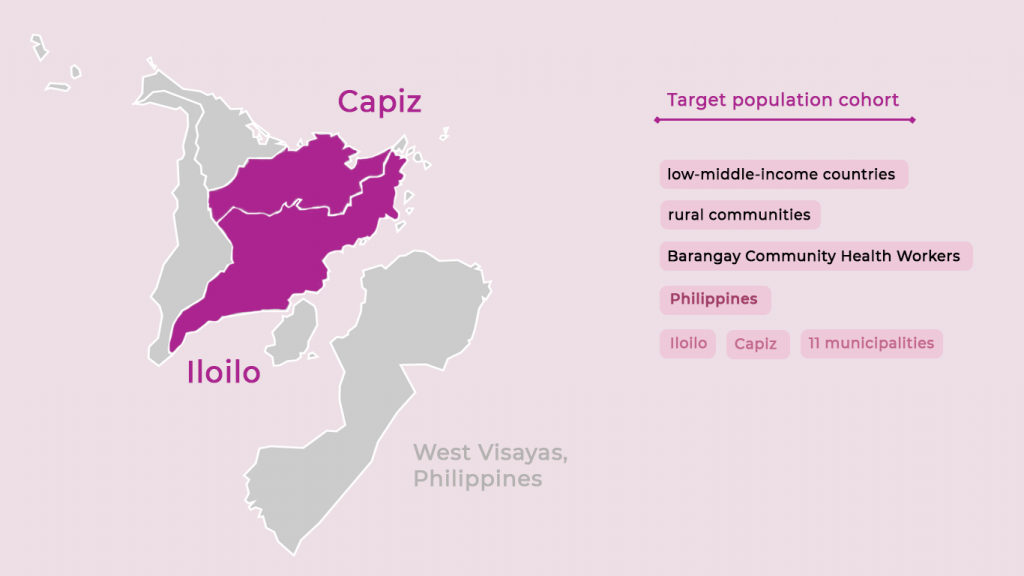
- To improve the health outcomes in the target communities across three areas
- Non-communicable Diseases (NCD)
- Infectious Diseases (ID)
- Maternal and Child Health (MCH)
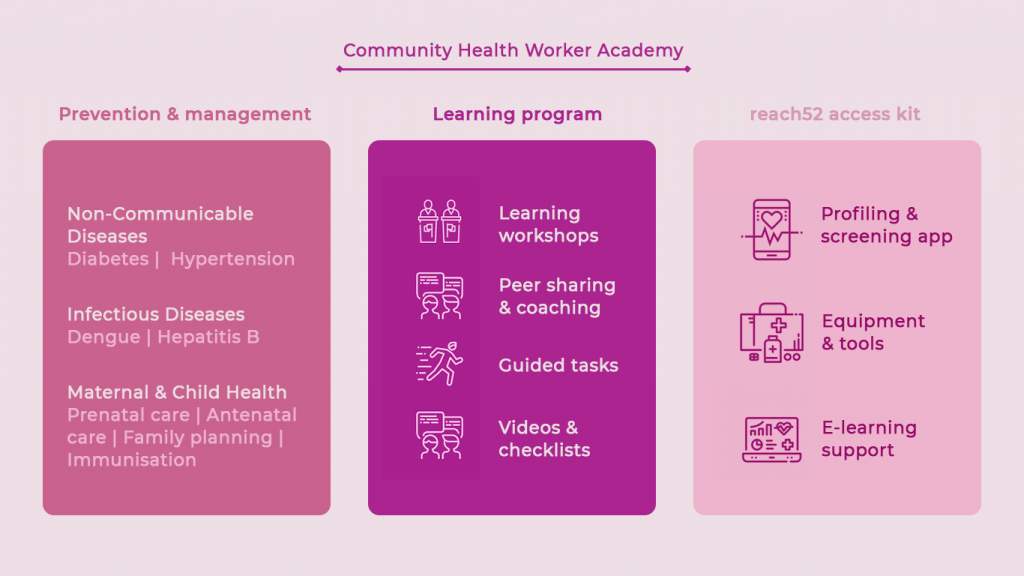
A blended learning program combining four in-person modules with digital learning channels was designed to equip the Agents with the skills and mindsets they need for prevention and management in the priority health areas. To provide integrated care through these distributed interpersonal community health teams, they were also provided with health screening devices and equipment through reach52 access diagnostics kits.
This innovative model was powered by the reach52 access “offline-first’ app designed for use in lower-resourced, and disconnected regions. At the end of this rigorous four-month intensive program, “Digitised” Agents would graduate with the capabilities to deliver health prevention, advice, screening and referrals needed in their communities. This model will decentralise quality primary healthcare work in rural and disadvantaged areas to our next-generation of front-liners working more closely to residents in their community.
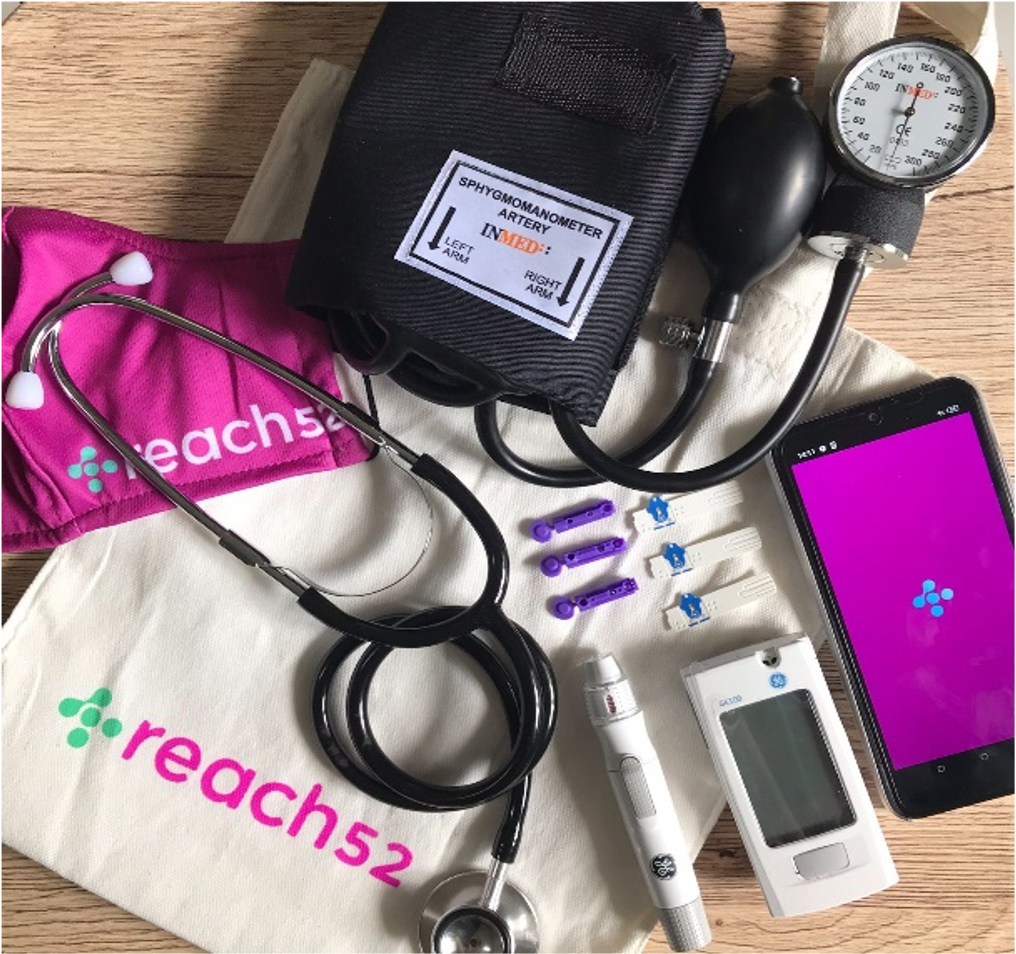
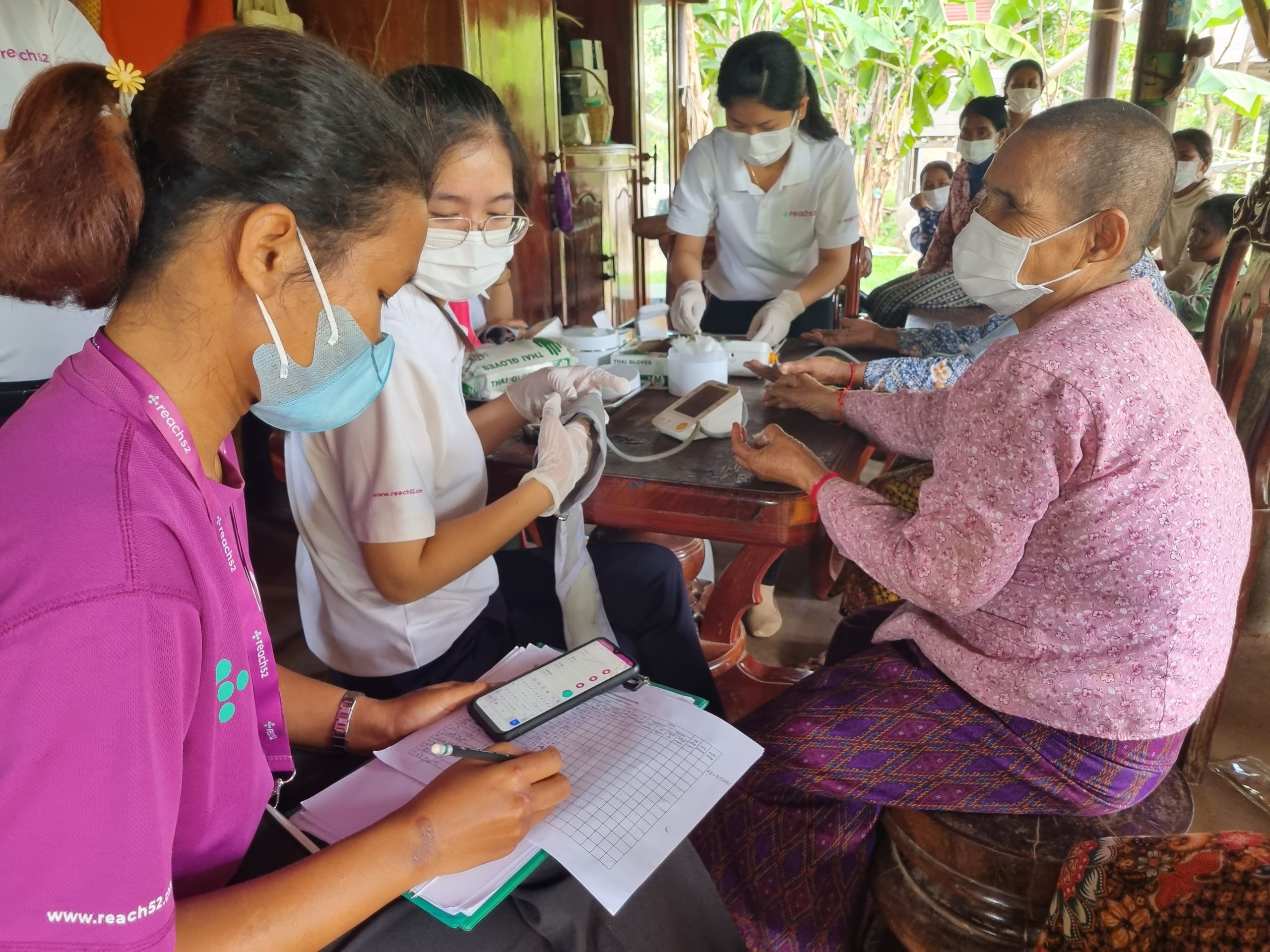
Access kits
Each Agent is equipped with an Access Toolkit that is composed of essential medical devices to enable them to perform their role better within their assigned healthcare areas. This includes a complete handbook of the modules, a blood pressure monitor, stethoscopes, glucometers, lancets, and strips, weighing scales, Hepatitis B rapid test kits, reproductive health products, and face masks.
Use of digital tools in rural communities
- Installed and created 1,226 reach52 access app accounts to ensure all villages are connected and empowered to record engagements via the platform
- Loaned 155 phones to Agents without mobile devices so each would have equal opportunities to learn and be trained
- Employed an interactive Facebook chatbot that reached about 5,014 residents
- Uploaded our training sessions on the reach52 access app so that Agents can access the modules remotely, especially during the pandemic
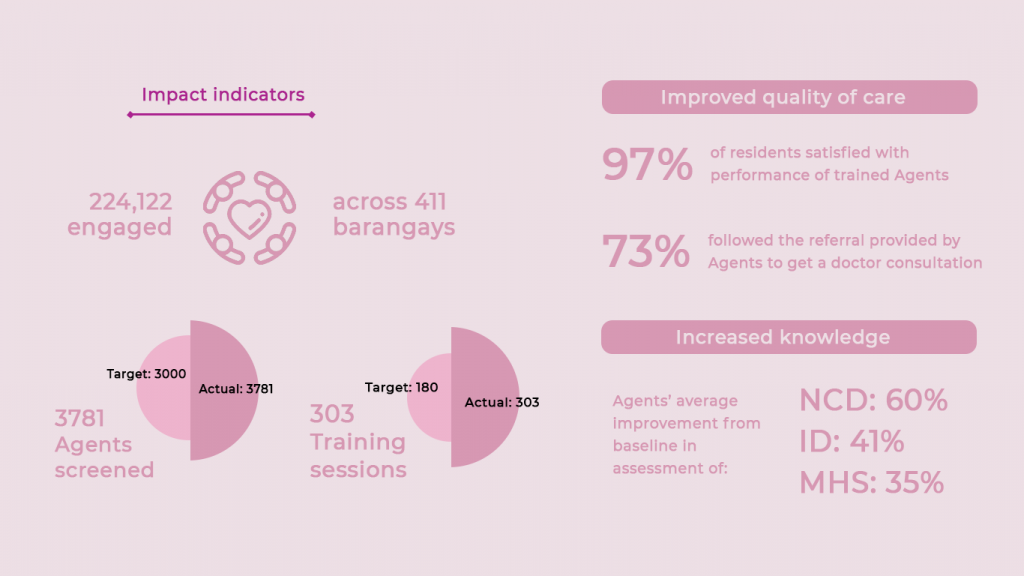
Insights
1. Ramping up digital tools during the COVID-19 pandemic
Delays hampered our scheduled training sessions due to lockdowns in communities and attendance were also affected due to financial, location or personal reasons dropping to 70% retention rate per module, so to reach community healthcare workers who missed some of the training sessions, the team deployed our modules and materials into the reach52 access e-learning platform and initiated a Facebook Group Class by posting the relevant materials in the group. These digital channels have sped up the team’s engagement rate in upskilling the healthcare workers efficiently, enabling us to reach the target for the program.
2. Addressing digital literacy
We observed that Agents typically show hesitancy at first given the unfamiliarity to a new digital platform and the resulting learning curve. However they showed willingness and interest to learn as the team showed them the salient features of the app which are easy to navigate. Over module sessions, the team has noticed improvement among their performance in using the platform, for example improved time navigating the forms and completing the health status profiles of their residents. We also use this opportunity to continue improving the interface of the app, making it simpler to interact with.





